Today I’m going to tell you about my first experience with blockchain and I ask you not to judge me. In 2016, I was in Cannes participating in one of the first events aimed at the eSports market, which brought together speakers from all over the world. Among them an IBM engineer specializing in blockchain.
We became friends and he spent the five days of the event trying to explain to me what blockchain was and the rise of Bitcoin that would happen in the coming years.
My English wasn’t very good at the time and mixed with my lack of knowledge in technology, I tried hard, but I couldn’t understand anything. I didn’t even understand why that IBM professional would give a speech at an eSports event.
The fact is that if I had understood I could have retired the following year.
I’ll explain why I could have gotten rich. On July 15, 2016, 1 Bitcoin (BTC) was quoted at $665, according to Cointelegraph Markets. On July 15, 2020, Bitcoin was worth an average of $9,250. That is, the virtual currency reached an appreciation of 1,390% in four years.
So that you absolve me, I publish here the definition of blockchain from the IBM website: “blockchain is an immutable and shared ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and controlling assets in a business network”. If you heard this at an eSports event, would you understand? Even worse would be to understand this definition in another language, right?
Now that I’ve told my story, let’s get to the facts. The first digital currency (cryptocurrency) released using blockchain technology was Bitcoin. As I have shown here, over the years more people have come to understand the cryptocurrency market and demand has increased so much that the value of one Bitcoin has appreciated by up to 200,000,000%.
So that you don’t miss the boat like I did, I decided that on this site we’ll explain everything in detail.
What is Bitcoin

Before proceeding, I define here what Bitcoin is. It is the first virtual currency. As such, it is a decentralized and free currency that does not need the interference of banks. We can say that it is electronic money for point-to-point financial transactions, which only exists virtually – there is no way to pick it up, nor count bills.
Historical records say that Bitcoin first appeared in an article by a group of programmers under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, on October 31, 2008. In 2009, Bitcoin was first used with Nakamoto mining the original block with the first 50 BTCs, but he was unable to buy anything with them.
The first Bitcoin transaction was recorded the following year when an American programmer from Miami launched a challenge on the Internet. The goal was to make the first purchase with a digital currency. And he did!
On May 22, 2010, Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 bitcoins for two pizzas. A decade later, in 2020, the 10,000 coins were valued at $600 million.
Over the years, Bitcoin had a huge appreciation, reaching 200,000,000%, but it was still restricted to technology professionals.
Because of this first transaction, every year on May 22 the internet world celebrates “Bitcoin Pizza Day”.
It’s important to record here a failed attempt that happened before Bitcoin. The story goes that in 1982, that is 27 years before Nakamoto’s white paper, university student David Chaum, a doctoral candidate at the University of California at Berkeley, described a blockchain database in his dissertation.
This study resulted in DigiCash, founded by Chaum, in 1989. Years later, in 1995, he launched the DigiCash cryptocurrency, which had many of the characteristics of Bitcoin. But his business went bankrupt soon after.
What is the Relationship Between Blockchain and Bitcoin?
The origin of the blockchain is linked to the origin of Bitcoin. Blockchain is the technology behind Bitcoin and other virtual currencies, also called cryptocurrencies or virtual currencies.
Blockchain is a database that contains the history of whatever information it was designed to store. Therefore, it also serves to keep NFTs (non-fungible tokens) unique. I think everyone remembers the virtual monkeys that became famous. They were NFTs.
In a simplified way, it is a technology composed of a chain of blocks – this explains its name and the images that appear on the websites to illustrate the articles. As a technology, it groups together a set of information that is connected to each other by cryptography, hence the name cryptocurrency.
But in addition to financial transactions such as crypto P2P, direct exchange of currencies between buyers and sellers, blockchain can be used by e-commerce companies and technology platforms to securely validate transactions.
Amazon’s Definition
On its website Amazon explains this concept much better than IBM. “Blockchain technology is an advanced database engine that enables transparent sharing of information across a company’s network. A blockchain database stores data in blocks linked together in a chain. The data is chronologically consistent because it is not possible to delete or modify the chain without network consensus”.
In this way, it is possible to use blockchain technology to create an unalterable or immutable ledger and thus monitor various transactions, such as orders and payments, with ledger being the ledger cited by IBM.
In blockchain transactions, a ledger means a system for keeping records of the balances of the various participants and of all transactions that occur on the network.
Through cryptography, the blockchain system offers integrated mechanisms that protect it from unauthorized transaction entries and allow you to consistently and share all transactions made within it. Thus, financial transactions and other operations can be done securely.
Security is guaranteed as the blockchain verifies transactions. The blocks store details and identification of the transfer process of digital assets, which in a matter of seconds pass from one owner to another. In this type of transaction, it is not necessary to use a bank.
Banks Are Using This Technology
But that doesn’t mean banks are giving up using blockchain technology. Traditional financial systems such as banks or stock exchanges use blockchain services to manage payments, accounts and the online trading market.
In Brazil, financial institutions such as Santander, Itaú and BNDES (National Bank for Economic Development) already use it as a way to reinforce security in some transactions.
Blockchain and DeFi go together like beer and pizza. DeFi applications track secure transactions while eliminating slow middlemen – such as financial institutions.
What is DeFi
DeFi is a set of financial services and products. Among them we have loans, transfers and payment systems, which run on a blockchain.
DeFi apps are available for lending and borrowing, cross-border transfers, investments and other operations.
Technology Applied to Other Markets
Health is one of the areas that is being revolutionized with the use of blockchain. The blockchain database architecture favors the storage of personal health data. For the data to be accessed by the patient, the doctor, the pharmacy, they just need to connect to the Internet. Each end of the process can search and store data in the same location. Works like a private Google Drive.
Blockchain technology can be used by insurance companies to reduce fraud and expedite claims reimbursement.
It can also be applied in the voting process in elections.
One of the applications that I liked the most was in IPs – intellectual property records. For over 20 years I’ve seen video game developers worried about piracy. Ending the piracy of music, movies, video games and artwork is fantastic.
Distribution via the blockchain could make each copy of a digital media file unique and provide a convenient mechanism for viewers to make micropayments directly to creators or distributors.
The same logic is being tested in Poker, gambling and online gambling. The blockchain can create a register that establishes the randomness of dice rolls in all types of games involving money. The blockchain can record players’ strengths in roleplay games and their winnings in gambling.
In video games, the blockchain can be used for your purchase in online stores, as well as for customizations and other functionality, created through non-fungible tokens.
Large companies are already using this technology and creating their own versions of the metaverse.
Companies using Blockchain
Nearly half of the companies on the Forbes Top 50 Blockchain list are not based in the US, and 14% are in China, where technology is taken seriously.
An interesting point raised by the magazine is the use of a large number of registered and real estate agents around the world. Blockchain is used for verifying insurance claims and in buying and selling real estate.
This technology has even become vital for supply chains, whether it’s certifying that products don’t come from conflict zones or tracking auto parts. In this case, the French Renault already uses it.
Read more about blockchain:
- All about Blockchain Technology and its Role in the Metaverse
- The Blockchain Gaming Revolution
- Blockchain ecosystem: What is it and what are its elements?
Blockchain and Video Games
Combining blockchain and Artificial Intelligence, from the much-discussed GPT Chat. Delisyum, publisher of Web3 games, is working on Lucy’s beta test. As the first AI-powered Web3 operating system, Lucy can answer questions about the crypto world and help the player to utilize all kinds of on-chain products without permission through natural language. Very soon, Lucy will join the next 100 million users in the crypto world.
Blockchain can be used in games, highlighting the individuality of each player in a way that has never been seen before. Through it, each player can obtain items or avatars that are unique and impossible to be obtained by any other player. New content is relevant in DLC sales and microtransactions, and this completely unique new element can offer players a truly rare item or avatar that has its own value.
The first popular digital blockchain game heard about was Cryptokitties. In it, players can adopt, breed and trade virtual cats with unique features.

The game runs on the Ethereum blockchain and smart contracts are formed every time a cat is adopted, bred or traded. A token is also issued to the user. This NFT gives the player full ownership of a virtual cat. The goal of the game is to breed cats to sell them. Some cats have sold for over $100,000 because of the rarity of their features.
The success of Cryptokitties in 2017 prompted several Chinese companies to look into the technology to see how they could develop their own successful blockchain games.
In addition to gaming giants like Tencent and NetEase, technology and internet conglomerates, among them Baidu and Xiaomi, have launched their own blockchain games.
“Laici Dog”, Baidu’s first game, hit the Chinese market in February 2018 and was developed by its in-house blockchain team. The game is similar to Cryptokitties, with puppies and no cash transactions. Coins are exchanged for Baidu products. Xiaomi preferred more endearing little animals and launched “Crypto Rabbits”.
NetEase, a major publisher of PC and mobile games announced Lucky Cat, its first blockchain game, in 2018. Lucky Cat aimed to capitalize on the success of Cryptokitties. However, the game was terminated after just a few days of testing and users were refunded. But the company keeps trying and recently announced that it is working on a game that could be the first triple A of Web3.
Last but not least, Tencent, the world’s largest game company, released in 2019 its first blockchain game on iOS and Android mobile platforms. Let’s Hunt Monsters combines blockchain technology, augmented reality (AR) and location-based services (LBS), the same as Pokémon GO.

Despite being restricted to China, Tencent’s Let’s Hunt Monsters, a China-only launch, was a success and in the year of release surpassed $50 million in player spending on iOS, according to estimates by Sensor Tower Store Intelligence.
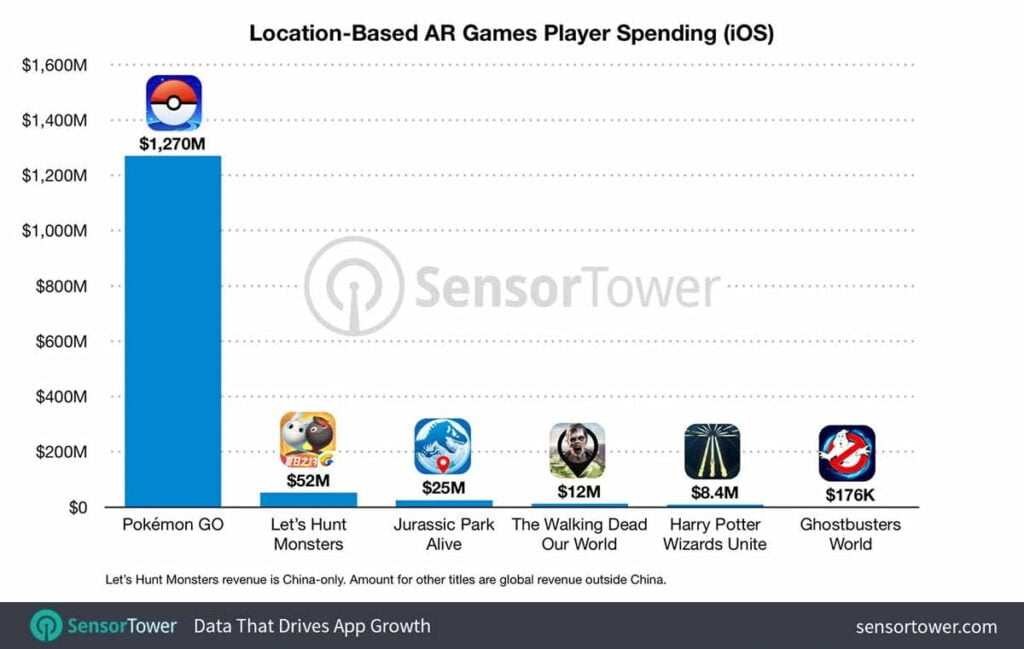
The study revealed another interesting fact. Unlike other blockchain games, Let’s Hunt Monsters is not based on any pre-existing intellectual property, but that hasn’t stopped Chinese iOS gamers from spending more than twice as much on the blockchain title as they did on Jurassic World Alive, which does not use this technology.
Translation by Laura Bonci






